
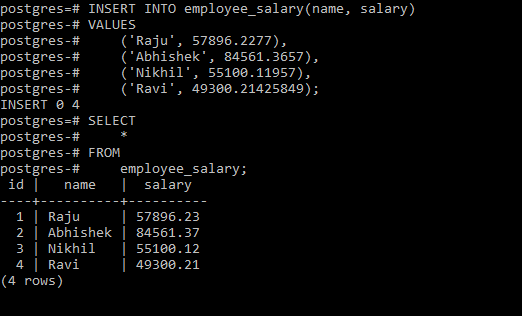
To optimize the performance of ALTER TABLE, optimize the setting that deals with the inner working of data within your database instance: in MySQL, that’s innodb-buffer-pool-size.
The way ALTER TABLE works is a little different to SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE queries that you are so used to – once the statement is used, your database management system will go through a couple of phases (for convenience, the original table that you run queries on will be called A, and the other will be called B): Rename columns, add constraints, and do a whole bunch of other things.īy now, you should get it – the ALTER TABLE statement can perform pretty much any action related to modifying data within a table.change the VARCHAR data type to INT on a certain column, etc.) Change the row format of rows in a table.

Specify options within a table (one can specify the size of AUTO_INCREMENT, specify the average row length, the default character set, default collations, set comments, set directories that hold indexes or data, etc.).Add, drop, discard, import, truncate, reorganize, repair, remove, or otherwise modify partitions.Add, modify, or delete indexes from a table.Add, modify, or drop columns belonging to a certain table.The ALTER TABLE statement can be used to: Rather simple, right? This simple statement has a lot of use cases – care to go through them with us? The Use Cases of ALTER TABLE


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
